Kidney stones are a common disease in Singapore, affecting 1 in 10 individuals. Understanding the different types of kidney stones, as well as their causes and symptoms, can help you take proactive steps toward prevention and early treatment.
What Are Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of salts and minerals that develop within the kidneys. They form when
substances like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid become overly concentrated in the urine, leading to
crystallisation and clumping. While high concentrations are a primary factor, stones can also form due to
other influences, such as pH imbalances and genetics.
Kidney stones vary in size—from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. They can affect any
part of the urinary tract, from the kidneys to the bladder. While small stones may pass through the urinary
tract without much discomfort, larger stones may obstruct the urinary tract and cause severe pain.
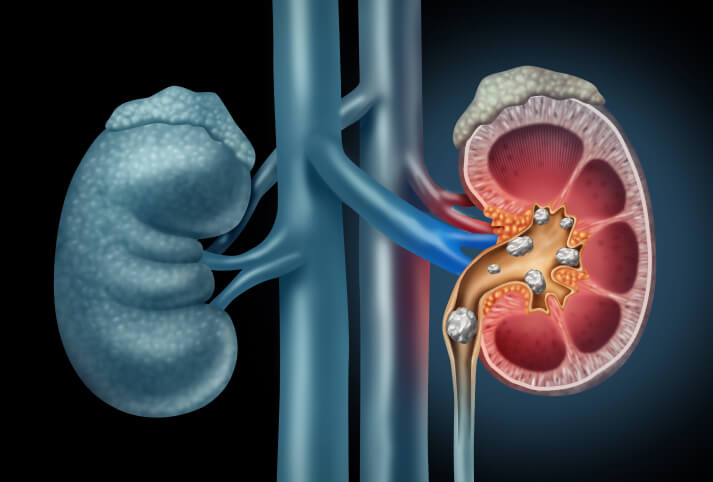
What Are the Different Types of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are classified based on their crystal composition. This classification is essential for identifying the underlying causes of stone formation and preventing recurrence. The four main types of kidney stones include:
Calcium stones are the most prevalent type of kidney stone, accounting for 70–80% of cases. They are typically caused by an excess of oxalate, which is common in some fruits, vegetables, nuts and chocolate.
Uric acid stones form when there is too much uric acid in the urine. Uric acid is a waste product, formed when the body breaks down substances called purines from food and cells. These stones are more common in people with gout or a high-protein diet.
Struvite stones are less common and are caused by bacterial infections. They can grow quickly and become very large, sometimes filling the entire kidney.
A rarer form of kidney stone, cystine stones, develops in people with the inherited condition cystinuria. This condition results in the leakage of excessive cystine (an amino acid) into the urine, causing stones to form.
Book an appointment at our clinic today to address kidney stones.


What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Symptoms of a kidney stone may not manifest until it shifts within the kidney or travels into the ureter—the conduit that links the kidney and bladder. Once this happens, the following signs and symptoms may present themselves:
- Severe, sharp pain on either side of the lower back
- Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin
- Persistent, vague pain or a stomach ache that does not go away
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urination
- Blood in the urine
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Foul-smelling or cloudy urine
- Difficulty urinating
- Urinating in small amounts
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment for kidney stones can help prevent complications and relieve symptoms effectively.
What Are the Risk Factors for Kidney Stones
Several factors may increase a person’s risk of developing kidney stones. These include:
Book a consultation with us for all your kidney stone concerns.

Our Urologist
FRCS(UROL) (RCPSG), FAMS(UROL)
Dr Lincoln Tan is a consultant urologist and accredited robotic surgeon at Mount Elizabeth Hospital. He has expertise in kidney and urinary tract stone removal, offering both non-invasive extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and minimally invasive treatments. Dr Tan prioritises high stone-free rates while ensuring patient-centred care through attentive listening and clear communication for the best possible outcomes.
Let us help you recover to a stone-free life.
Location
6 Napier Road #05-03,
Gleneagles Medical Centre,
258499, Singapore
Contact Us
| Phone |
: +65 6732 6503 |
| : info@tanurology.com.sg |
